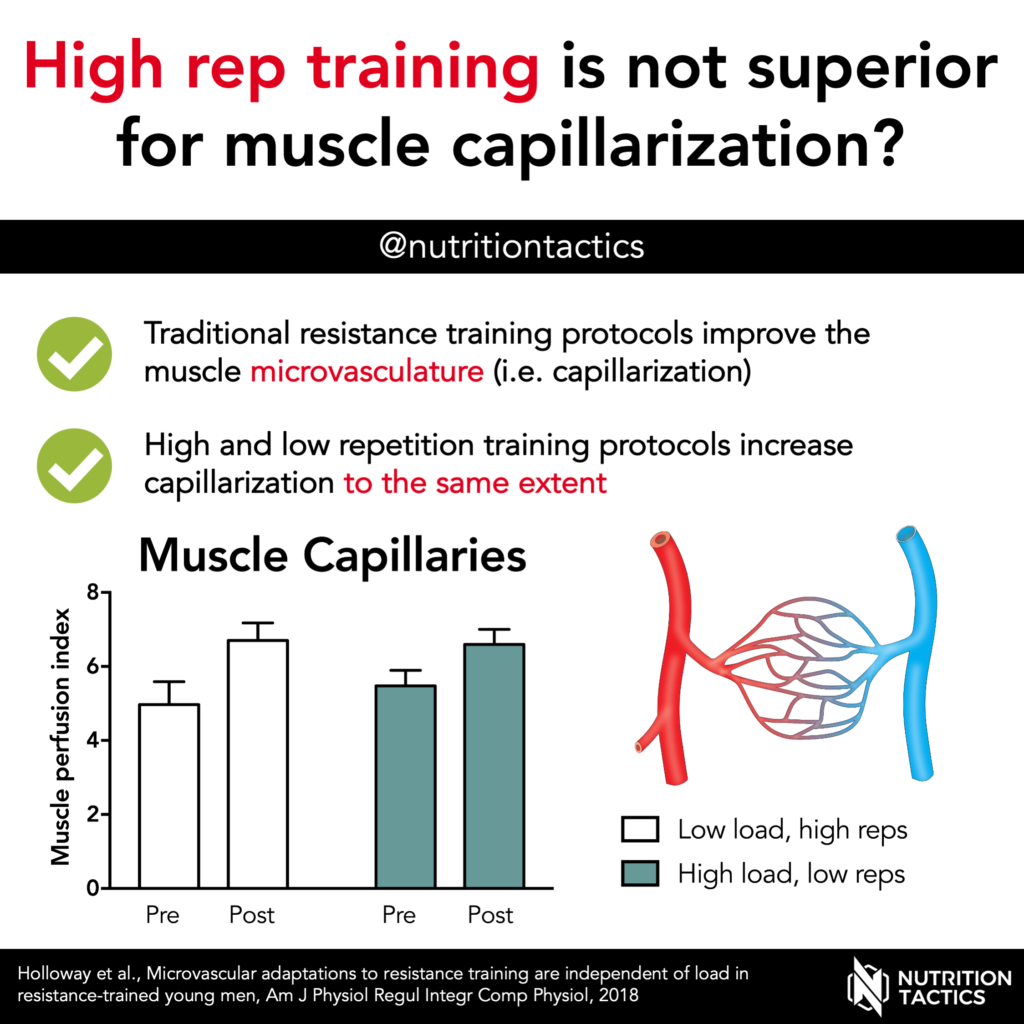
Are high rep resistance training protocols superior to increase muscle capillarization?
Muscle capillaries (the smallest blood vessels) are responsible for the delivery of oxygen, nutrients, and growth factors to the cells. Therefore, increasing the number of capillaries results in better perfusion and a better delivery of these compounds to the muscle fibers.
[Read more…] about High rep training is not superior for muscle capillarization?