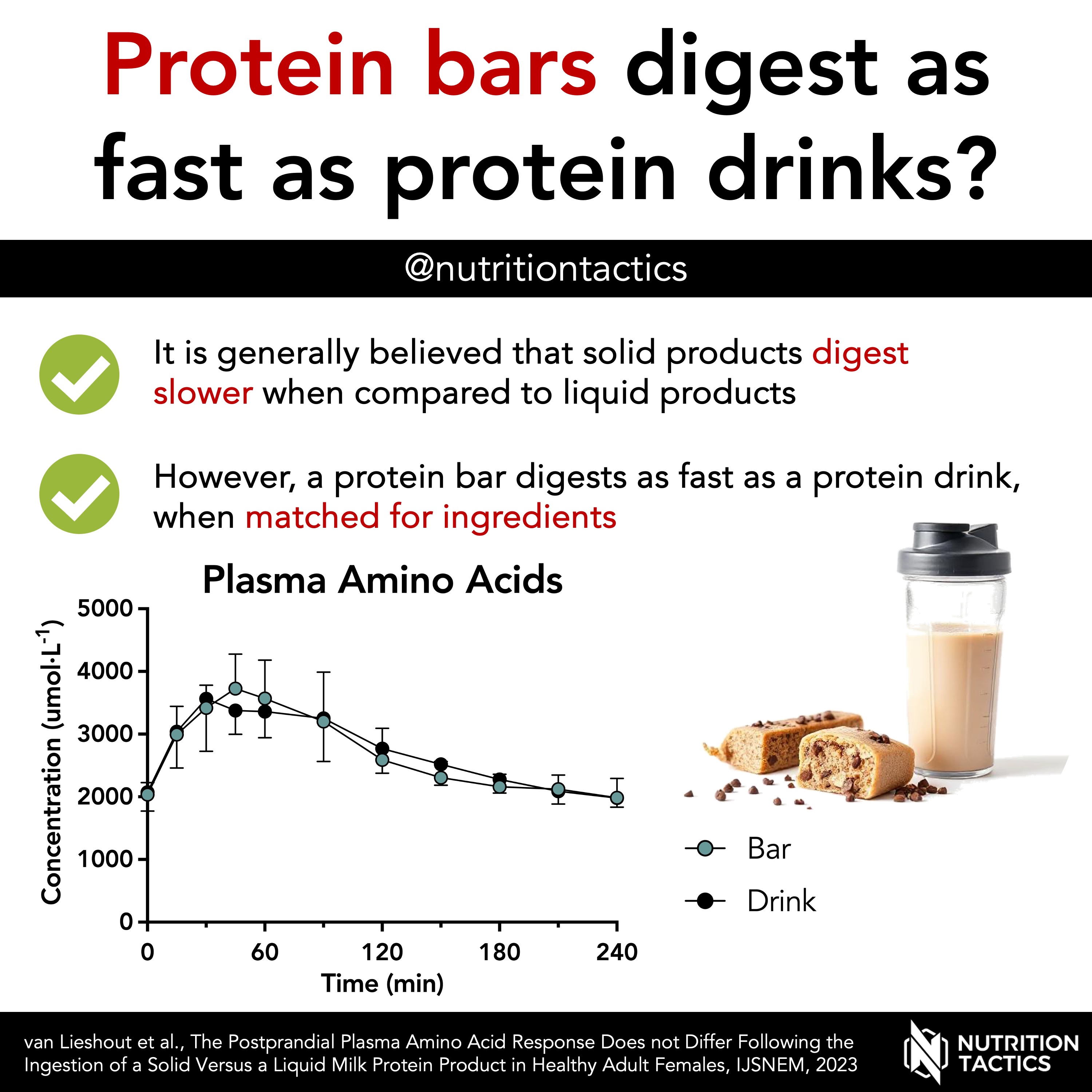
It is generally assumed that solid foods are digested more slowly when compared to liquid foods. However, solid foods typically differ from liquid foods not just in food form (liquid vs solid), but also in type of protein, other nutrients, and energy content. Therefore, it was unclear if the form (liquid vs solid) as an isolated factor impacts protein digestion and absorption.
In this study, we compared the plasma amino acid response between 20 g of milk protein as bar or drink in 12 healthy young women. Both products were specifically designed for this study to allow the ingredients to be matched as good as possible.
Key findings:
- The plasma amino acid response did not differ between the liquid and solid treatments
- No differences in hunger ratings were observed between the treatment
What does this mean?
Our data suggest that the food form (solid vs liquid) does not impact the digestion and absorption of protein. It should be noted that the protein bar treatment also drank water (although we don’t think this impacted the results).
Keep in mind that a protein drink and bar are typically not matched for ingredients in practice. Protein bars often contain collagen protein for texture and a chocolate solid outer layer. Therefore, the average protein bar will likely result in a slightly slower digestion and absorption of amino acids when compared to an average protein bar.
Next infographic in the protein series:
High-protein ultra-processed foods result in overeating?

Leave a Reply